The Kemle Family
Genealogy and History
Kemle DNA
Darrel Kemle had his DNA tested by the National Genographic Project. They can identify a male's deep ancestry using the Y-Chromosome. Only males can determine their deep ancestry using the Y-chromosome. But don't despair ladies, the results are available here for you to see too. Darrel sent in swabs from the inside of his cheeks which were analyzed for DNA markers. The DNA tests show that Kemles belong to Haplogroup I1.
The following results are from the Genographic project at https://genographic.nationalgeographic.com/genographic/index.html and enter Darrel Kemle's Genographic Project Kit ID "FWH73L3EUL" to log in.
Kemle Genetic Sequence
|
Type
Y-Chromosome
How to Interpret Your Results |
Kemle Genetic History
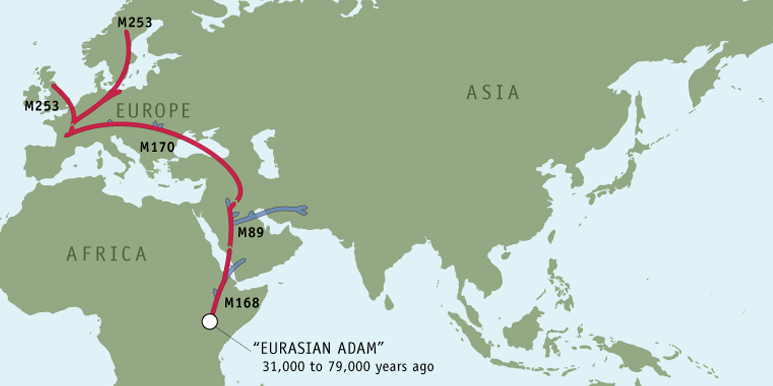
Your Y-chromosome results identify you as a member of haplogroup I1 (M253).
The genetic markers that define your ancestral history reach back roughly 60,000 years to the first common marker of all non-African men, M168, and follow your lineage to present day, ending with M253, the defining marker of haplogroup I1. Some in this lineage also carry the markers P40 and M227.
If you look at the map highlighting your ancestors' route, you will see that members of haplogroup I1 carry the following Y-chromosome markers:
M168 > P143 > M89 > L15 > P123 > M170 > M253
(Less is known about some markers than others. What is known about your journey is reflected below.)
What's a haplogroup, and why do geneticists concentrate on the Y chromosome in their search for markers? For that matter, what's a marker?
Each of us carries DNA that is a combination of genes passed from both our mother and father, giving us traits that range from eye color and height to athleticism and disease susceptibility. One exception is the Y chromosome, which is passed directly from father to son, unchanged, from generation to generation.
Unchanged, that is unless a mutation—a random, naturally occurring, usually harmless change—occurs. The mutation, known as a marker, acts as a beacon; it can be mapped through generations because it will be passed down from the man in whom it occurred to his sons, their sons, and every male in his family for thousands of years.
In some instances there may be more than one mutational event that defines a particular branch on the tree. When geneticists identify such a marker, they try to figure out when it first occurred, and in which geographic region of the world. Each marker is essentially the beginning of a new lineage on the family tree of the human race. Tracking the lineages provides a picture of how small tribes of modern humans in Africa tens of thousands of years ago diversified and spread to populate the world.
A haplogroup is defined by a series of markers that are shared by other men who carry the same random mutations. The markers trace the path your ancestors took as they moved out of Africa. It's difficult to know how many men worldwide belong to any particular haplogroup, or even how many haplogroups there are, because scientists simply don't have enough data yet.
One of the goals of the five-year Genographic Project is to build a large enough database of anthropological genetic data to answer some of these questions. To achieve this, project team members are traveling to all corners of the world to collect more than 100,000 DNA samples from indigenous populations. In addition, we encourage you to contribute your anonymous results to the project database, helping our geneticists reveal more of the answers to our ancient past.
Keep checking these pages; as more information is received, more may be learned about your own genetic history.
Kemle Ancestral Journey: What We Know Now
M168: Your Earliest Ancestor
Fast Facts
Time of Emergence: Roughly 50,000 years ago
Place of Origin: Africa
Climate: Temporary retreat of Ice Age; Africa moves from drought to warmer temperatures and moister conditions
Estimated Number of Homo sapiens: Approximately 10,000
Tools and Skills: Stone tools; earliest evidence of art and advanced conceptual skills
Skeletal and archaeological evidence suggest that anatomically modern humans evolved in Africa around 200,000 years ago, and began moving out of Africa to colonize the rest of the world around 60,000 years ago.
The man who gave rise to the first genetic marker in your lineage probably lived in northeast Africa in the region of the Rift Valley, perhaps in present-day Ethiopia , Kenya, or Tanzania, some 31,000 to 79,000 years ago. Scientists put the most likely date for when he lived at around 50,000 years ago. His descendants became the only lineage to survive outside of Africa, making him the common ancestor of every non-African man living today.
But why would man have first ventured out of the familiar African hunting grounds and into unexplored lands? It is likely that a fluctuation in climate may have provided the impetus for your ancestors' exodus out of Africa.
The African ice age was characterized by drought rather than by cold. It was around 50,000 years ago that the ice sheets of northern Europe began to melt, introducing a period of warmer temperatures and moister climate in Africa. Parts of the inhospitable Sahara briefly became habitable. As the drought-ridden desert changed to a savanna, the animals hunted by your ancestors expanded their range and began moving through the newly emerging green corridor of grasslands. Your nomadic ancestors followed the good weather and the animals they hunted, although the exact route they followed remains to be determined.
In addition to a favorable change in climate, around this same time there was a great leap forward in modern humans' intellectual capacity. Many scientists believe that the emergence of language gave us a huge advantage over other early human species. Improved tools and weapons, the ability to plan ahead and cooperate with one another, and an increased capacity to exploit resources in ways we hadn't been able to earlier, all allowed modern humans to rapidly migrate to new territories, exploit new resources, and replace other hominids.
M89: Moving Through the Middle East
Fast Facts
Time of Emergence: 45,000 years ago
Place: Northern Africa or the Middle East
Climate: Middle East: Semiarid grass plains
Estimated Number of Homo sapiens: Tens of thousands
Tools and Skills: Stone, ivory, wood tools
The next male ancestor in your ancestral lineage is the man who gave rise to M89, a marker found in 90 to 95 percent of all non-Africans. This man was born around 45,000 years ago in northern Africa or the Middle East.
The first people to leave Africa likely followed a coastal route that eventually ended in Australia. Your ancestors followed the expanding grasslands and plentiful game to the Middle East and beyond, and were part of the second great wave of migration out of Africa.
Beginning about 40,000 years ago, the climate shifted once again and became colder and more arid. Drought hit Africa and the grasslands reverted to desert, and for the next 20,000 years, the Saharan Gateway was effectively closed. With the desert impassable, your ancestors had two options: remain in the Middle East, or move on. Retreat back to the home continent was not an option.
While many of the descendants of M89 remained in the Middle East, others continued to follow the great herds of buffalo, antelope, woolly mammoths, and other game through what is now modern-day Iran to the vast steppes of Central Asia.
These semiarid grass-covered plains formed an ancient "superhighway" stretching from eastern France to Korea. Your ancestors, having migrated north out of Africa into the Middle East, then traveled both east and west along this Central Asian superhighway. A smaller group continued moving north from the Middle East to Anatolia and the Balkans, trading familiar grasslands for forests and high country.
M170: Occupying the Balkans
Fast Facts
Time of Emergence: 20,000 years ago
Place of Origin: Southeastern Europe
Climate: Height of the Ice Age
Estimated Number of Homo sapiens: Hundreds of thousands
Tools and Skills: Gravettian culture of the Upper Paleolithic
Your ancestors were part of the M89 Middle Eastern Clan that continued to migrate northwest into the Balkans and eventually spread into central Europe. These people may have been responsible for the expansion of the prosperous Gravettian culture, which spread through northern Europe from about 21,000 to 28,000 years ago.
The Gravettian culture represents the second technological phase to sweep through prehistoric Western Europe. It is named after a site in La Gravette, France, where a set of tools different from the preceding era (Aurignacian culture) was found. The Gravettian stone tool kit included a distinctive small pointed blade used for hunting big game.
The Gravettian culture is also known for their voluptuous carvings of big-bellied females often dubbed "Venus" figures. The small, frequently hand-sized sculptures appear to be of pregnant women—obesity not being a problem for hunter-gatherers—and may have served as fertility icons or as emblems conferring protection of some sort. Alternatively, they may have represented goddesses.
These early European ancestors of yours used communal hunting techniques, created shell jewelry, and used mammoth bones to build their homes. Recent findings suggest that the Gravettians may have discovered how to weave clothing using natural fibers as early as 25,000 years ago. Earlier estimates had placed weaving at about the same time as the emergence of agriculture, around 10,000 years ago.
Your most recent common ancestor, the man who gave rise to marker M170, was born about 20,000 years ago and was heir to this heritage. He was probably born in one of the isolated refuge areas people were forced to occupy during the last blast of the Ice Age.
It's possible that the Vikings descended from this line. The Viking raids on the British Isles might explain why the lineage can be found in populations in southern France and among some Celtic populations.
M253: Surviving the Ice Age
Fast Facts
Time of Emergence: Roughly 15,000 years ago
Place of Origin: Iberian Refugia (Spain)
Climate: Ice Free Regions, or Refugia, During the Ice Age
Estimated Number of Homo sapiens: Approximately one million.
Tools and Skills: Late Upper Paleolithic
Some 20,000 to 15,000 years ago your ancestors, like many Europeans, sought refuge from the massive sheets of ice that covered much of the continent during the last ice age. They found temperate ice-free refugia, in which they could survive, on the Iberian Peninsula.
While your ancestral lineage was geographically isolated by ice the distinctive genetic marker M253 appeared in one of its male members. As the Earth warmed and the glacial maximum passed, some 15,000 years ago, the ice finally began its slow retreat. The refugia's dwellers left the peninsula and began to repopulate other parts of Europe that had once been covered by ice. They carried with them the unique genetic marker that defines haplogroup I1.
Today this marker is still found in high frequencies throughout northwest Europe, providing a genetic map of the physical paths your ancestors walked long ago.
This is where your genetic trail, as we know it today, ends. However, be sure to revisit these pages. As additional data are collected and analyzed, more will be learned about your place in the history of the men and women who first populated the Earth. We will be updating these stories throughout the life of the project.